
🧩 Introduction: Two Worlds, One Mission
One designs code. The other assembles parts. At first glance, they seem like opposite professions.
But if we look beneath the surface, we find a powerful truth: Both are designers of efficiency.
In the era of Industry 4.0, technology has transformed manufacturing. Today, collaboration between the digital and physical worlds is fundamental for productivity and innovation.
🔬 Technical Foundation / Theory
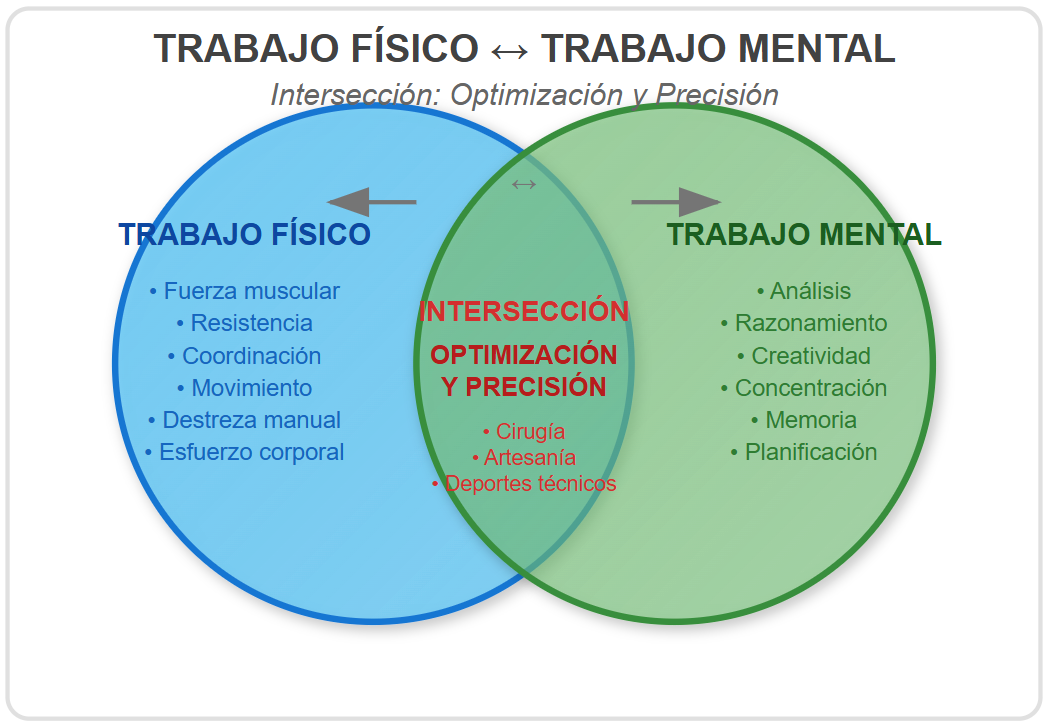
🔄 1. The Paradox of Difference: Are They So Distinct?
At first glance, the differences are obvious. However, when examining the structure of their routines and their goals, notable similarities are revealed, demonstrating a profound synergy in the realm of operational efficiency.
Structural Similarities
Well-defined routines
- 🧑🏽💻 Engineer: commits, deploys, pull requests
- 👨🏼🏭 Operator: shifts, stations, quality controls
High concentration on repeatable tasks
- 📊 Software: debugging, testing, refactoring
- 🏭 Production: assembling, verifying, calibrating
Precision goals and continuous optimization
- Both respond to KPIs, whether performance metrics, bugs, or units per hour. Industrial Engineering and Systems Engineering work hand-in-hand to design efficient and functional processes.
⚙️ 2. Industry 4.0 as a Meeting Point
Industrial automation is the key to Industry 4.0 and the bridge between these two worlds. Software has become the core of industrial operations, enabling system integration and real-time optimization.
The software designed by the engineer not only streamlines processes but also increases productivity and improves product quality, which directly benefits the operator and, ultimately, society. By taking on repetitive tasks, automation reduces errors and allows the operator to focus on functions requiring human judgment and decision-making.
🛠️ Practical Application: Symbiosis in Action
Let’s look at a concrete case: a manufacturing company implementing plant control software.
🎯 Interdependent Roles
- The software engineer designs the system that automates the lines and collects data (Big Data).
- The plant operator interacts with that system, inputs data, monitors machinery, and reports errors.
In this context, DevOps methodologies (Development and Operations) are gaining ground in the industry, integrating software development teams with the physical operations of the factory. This allows for smoother communication and a rapid response to the needs of the production environment.
Technical Snippet
{
"machine_status": "idle",
"operator_id": "OP-442",
"timestamp": "2025-07-12T10:32:00Z",
"event": "manual_override"
}That override wasn’t decided by a backend. It was executed by a person with critical judgment.
📊 Critical Analysis
| ✅ Advantages | ⚠️ Risks / Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Generates more robust products | Lack of communication between areas |
| Aligns digital innovation with physical reality | Underestimating the value of skilled physical labor |
| Fosters a culture of technical collaboration | Excessive dependence on one side of the process |
| Drives efficiency and competitiveness | Challenge of adapting to new technologies (learning) |
🎯 Tip: Design technology with the operational user, not for them. Collaboration is the foundation of efficiency in Industry 4.0.
🎯 Actionable Conclusion
Mind and hands do not compete. They collaborate.
The symbiosis between software ingenuity and operator experience is crucial for the future of production. This union not only optimizes processes but also brings significant value to society by generating more efficient and higher-quality products.
The next time you write a function, ask yourself: 🛠 Which operator in the real world does this impact? And if you are in a factory, ask yourself: 🧠 Who is behind the software I use daily?
👉 Share this article with someone who works in the “other world.” Let’s discuss more between both!
🧠 Recommended Resources
- 📖 The Toyota Way — about manufacturing efficiency and continuous improvement (Kaizen)
- 🎙️ Podcast: Software meets Industry — episodes on industrial automation
- 💼 Personal experience
📚 Consulted Sources
- Experiences of integration between PLCs and SCADA in real industrial environments
- Case studies of industrial automation with operational feedback
- Practical observations of DevOps teams in smart factories
- SPC Consulting Group: THE TOYOTA WAY: Las claves del éxito de Toyota.
- Grupo Alisios: Beneficios de la automatización industrial: Aumenta productividad y reduce costos.
- Ag-RobotX: La automatización industrial: claves para mejorar la eficiencia.
- IAT (Industria, Automatización y Tecnología): Industria 4.0 y desarrollo de software: Cómo plataformas como Velneo transforman el sector industrial.
- UFV (Universidad Francisco de Vitoria): ¿Cómo se relaciona la Ingeniería Industrial con la Ingeniería en Sistemas?